Heart Disease: Types, Causes, Symptoms and Treatment
- 07 Sep, 2023
- 394
- Medical tourism
The human heart is a delicately designed organ that supports the entire body. It is a muscular organ that is about the size of a closed fist and is located in the centre of the chest but somewhat to the left. The heart beats around 100,000 times every day, distributing 8 pints of blood throughout the body. This transports waste and supplies tissues and organs with blood that is nutrient- and oxygen-rich. Deoxygenated blood is delivered by the heart to the lungs, where it picks up oxygen and releases carbon dioxide, a waste product of metabolism. The circulatory system is made up of the heart, blood, blood vessels, arteries, capillaries, and veins.
Heart
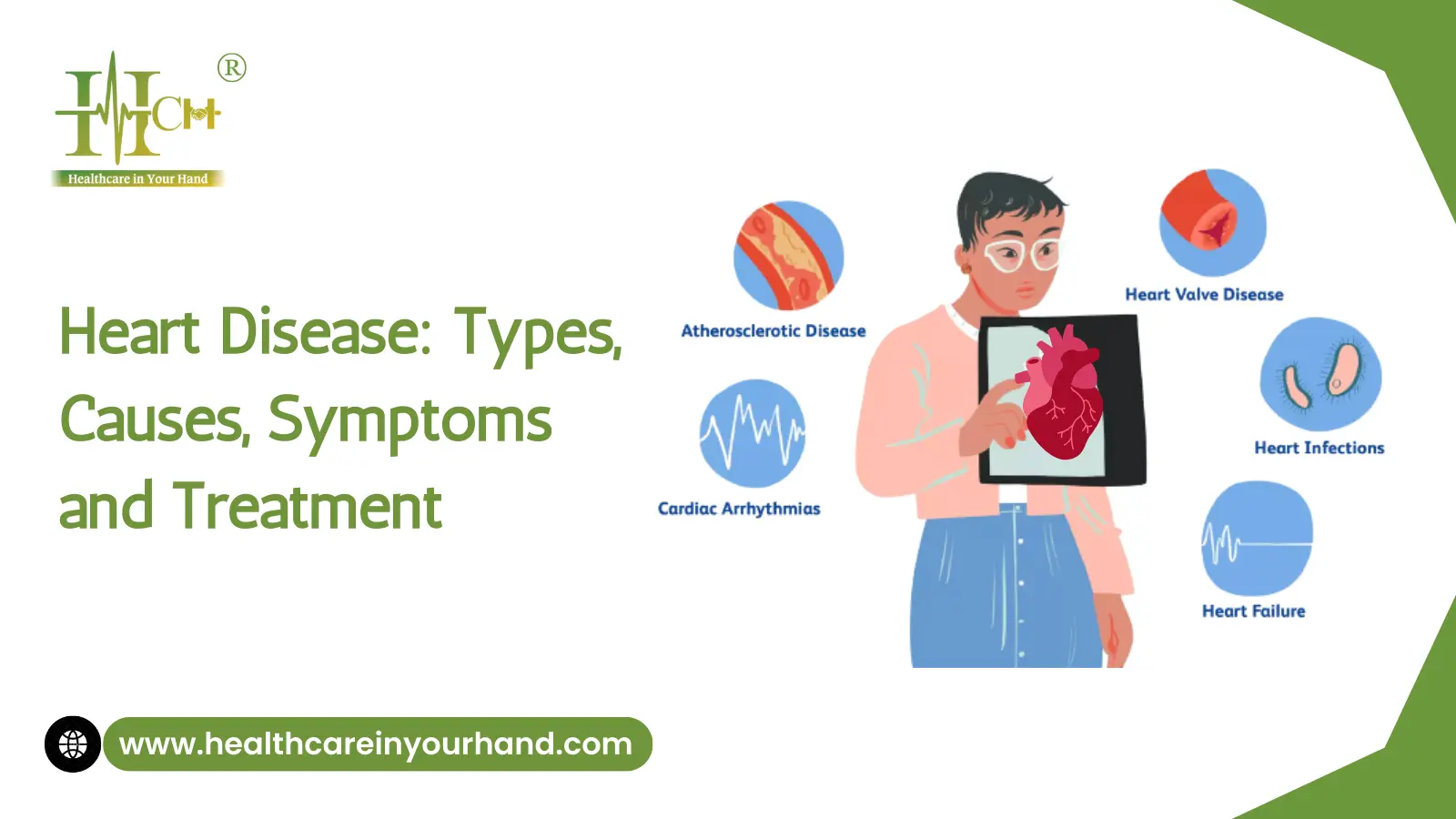
Disease and Its Types:
CAD, Heart valve disorders, Heart
attack, Heart failure that causes heart squeezing and makes it difficult to
relax, Arrhythmias or irregular heartbeats, congenital heart disease, abnormal
heart muscle or cardiomyopathy, and problems with the pericardium (the sac
filled with fluid that surrounds your heart) are some of the types of heart
related ailments.
Let’s discuss different types of
possible heart disease and it’s symptoms in detail.
1- Congenital
heart disease:
Some individuals are born with a congenital
heart problem. It mostly affects the heart's blood arteries, valves, and walls.
Heart problems that can occur at birth include the following.
• Abnormal Heart valves: These
valves may leak blood or fail to open properly.
• Septal defects: A hole exists
in the heart's wall between either the lower or upper chambers.
• Atresia: A cardiac valve that
is absent.
Bluish lips and complexion,
breathlessness, eating difficulties, abnormally low birth weight, chest pain,
and delayed growth are just a few of the signs that newborns with congenital
heart disease may exhibit.
2- Ischemic
heart disease:
When the coronary artery is blocked,
the heart cannot receive enough blood, which causes a heart attack. In
medicine, a heart like this is referred to as ischemic. Possible signs
and symptoms of ischemic heart disease are as following.
• Chest pain: This is described
as a tightness that may spread to the base of your neck or your arms. Shortness
of breath, cold sweats, and nausea may or may not be present.
• Palpitations: If you have
ischemic heart disease, you probably feel your heart pounding in your chest and
have a rapid heartbeat.
• Shortness of breath, sometimes
referred to as dyspnea, impairs the heart's ability to pump blood to the
rest of the body. This causes the blood to stagnate in the heart, which makes
breathing challenging.
• Loss of consciousness: This
can happen when the heart is unable to adequately pump blood to the rest of the
body.
• Both cold sweats and nausea can
strike at once or separately. This is the nervous system's attempt to react to
ischemia.
3- Coronary
Artery Disease or CAD
CAD is brought on by
dysfunctional blood arteries that carry blood to the heart. As a result, there
is a disruption in the flow of oxygen, blood, and other vital nutrients. This
occurs as a result of cholesterol build-up on the artery walls. When you have
CAD, it's possible to develop blockages in your coronary arteries, which can
result in a reduction in the blood flow to your heart muscle and prevent it
from receiving the oxygen it requires. The condition that often causes the
disease to start is atherosclerosis, also known as hardening of the arteries.
Angina, a chest ache that is caused by CAD may lead to a heart attack.
The most typical CAD symptoms include
angina, which might feel tight or pressing in the left or middle of the chest.
Another symptom is breathlessness. If your heart isn't pumping enough blood,
you'll experience exhaustion. Additionally, a heart attack will occur when the
coronary artery is totally obstructed.
4- Heart Failure
It occurs when a person's heart
continues to beat, but not as well as it should. Problems with the pumping or
relaxing function can lead to congestive heart failure, a specific kind of
heart failure. Coronary artery disease, hypertension, arrhythmias, and other
problems that go untreated can all lead to heart failure. The heart's capacity
to rest or pump correctly may be compromised by several diseases. Heart-related
illnesses should be treated as soon as possible to reduce the risk of
complications, as heart failure can be fatal.
Common signs include coughing, fatigue,
weakness, dizziness, decrease in appetite, need urination at night,
palpitations or rapid or erratic heartbeat shortness of breath after lying
down or during physical activity enlarged or swollen liver or abdomen, swollen
ankles and feet, waking up from sleep after a few hours owing to breathing
difficulties, gaining weight.
5- Arrhythmias
An irregular heartbeat is known as an
arrhythmia. It takes place when the electrical impulses that regulate the
heartbeat are malfunctioning. The outcome may be an irregular heartbeat or a
heartbeat that is too fast or too slow.
A variety of arrhythmias exist, that
includes,
a- Tachycardia: heartbeat
that is too quick.
b- Bradycardia: This term
describes a sluggish heartbeat.
c- Contractions that start too
early: This is a heartbeat that starts too early.
d- Atrial fibrillation:
abnormal heartbeat
One could have a sensation like a
rushing heart or fluttering. Shortness of breath, Fainting or light-headedness,
Chest pain, and Fatigue can be other symptoms.
Arrhythmias can, in rare
circumstances, be fatal or have serious side effects.
6- Disease of
the Heart Valve
The four chambers of the heart, the
lungs, and blood vessels are connected by four valves that open and close to
control blood flow. A valve's ability to open and close properly may be
compromised by an anomaly. Your blood flow could be obstructed or blood could
leak as a result.
Chest pain, abdominal swelling, a
whooshing sound in the heart (or heart murmur), and severe tricuspid
regurgitation are all signs of heart valve dysfunction. Apart from these, you may also experience Fatigue and breathlessness, especially when
moving or when lying down. Your feet and ankles swelling, and you feel faint and
woozy.
7-
Aortic Stenosis
It is frequently referred to as a
failing heart valve or a narrowing of the aortic valve orifice and is one of
the most prevalent and dangerous valve disease issues. The left atrium's
pressure may be impacted by aortic stenosis, which limits blood flow from the
left ventricle to the aorta. It could be born with congenital valve
abnormalities, or it might develop over time as a result of calcium deposits or
scarring.
You could never have any symptoms if
you have mild aortic valve stenosis. Symptoms frequently take a long time to
become more obvious. There are specific signs for severe cases that are
important to note. They consist of breathing difficulties especially after
exercising, stiffness or pain in the chest experiencing dizziness or faintness
Fatigue, fluttering or rapid heartbeats, cardiac murmur
8- Cardiomyopathy
It is a condition that affects the
myocardium, or heart muscle. It stretches, thickens, or becomes stiff. It's
possible that your heart won't be able to pump properly. Potential causes
include viral infections, genetic heart abnormalities, adverse drug or toxin
reactions (including alcohol), and genetic heart conditions. Chemotherapy can
occasionally result in cardiomyopathy.
Heart
disease risk factors
You may be more susceptible to certain
diseases due to a variety of lifestyle and environmental variables. Significant
contributors include the following:
• High
cholesterol.
• Blood
pressure issues.
·
Type 2 diabetes.
• Unhealthy
diet.
• Substance
abuse disorders.
• Smoking
• Heavy
alcohol consumption
• Elevated
triglycerides
·
Diabetes and heart disease in the family,
• Food
Choices
Age, sleep apnea, a lack of exercise,
a high level of stress and anxiety, being overweight and obese, having leaky
heart valves, and having a history of preeclampsia during pregnancy are all
risk factors.
Heart
Disease Causes:
Causes of heart disease vary in
accordance to it’s type.
• A build up
of fatty plaques in the arteries is what causes coronary heart disease.
• Drug
interactions, diabetes, cardiomyopathy, mental stress, alcoholism, or smoking
can all contribute to irregular heartbeats.
• One month
after pregnancy, congenital cardiac abnormalities typically start to form in
the womb.
• Cardiomyopathy,
or an enlarged heart muscle, may be hereditary or brought on by the
accumulation of a protein called amyloid in the heart.
• Viruses,
parasites, and bacteria can all cause heart infections.
• Rheumatic
fever or conditions affecting connective tissue are the two main causes of
heart valve disease.
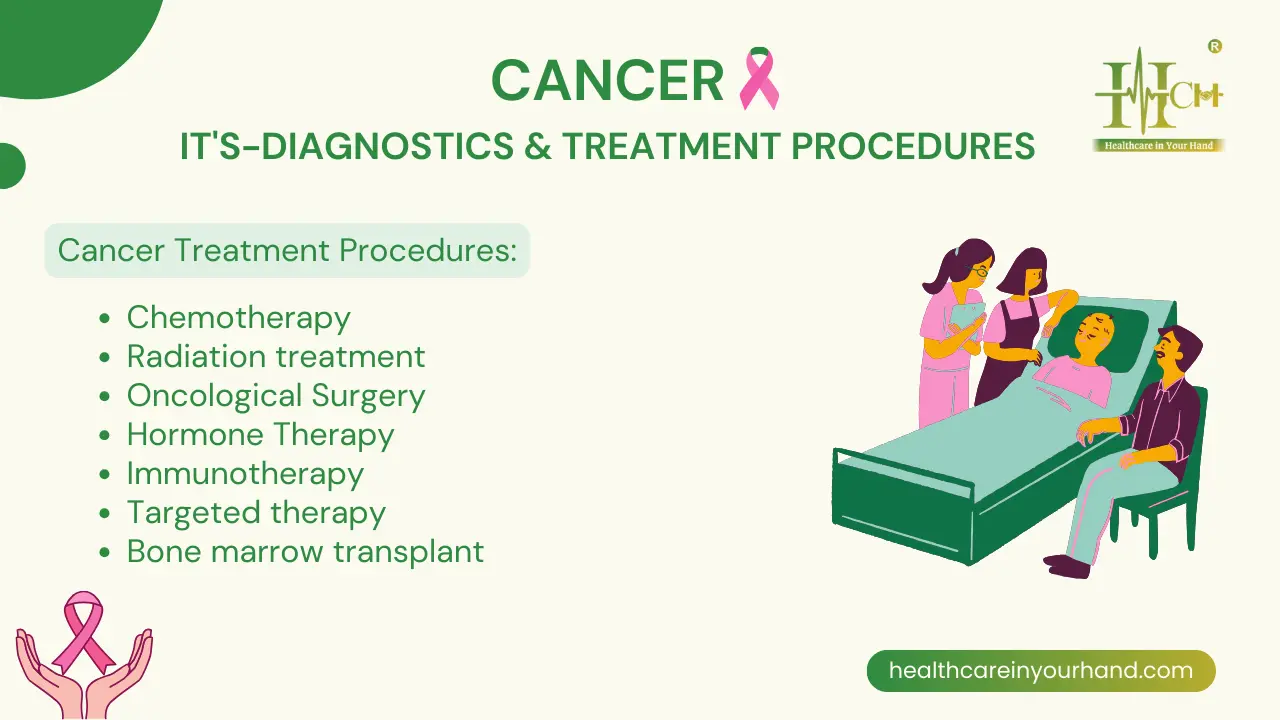
Treatment
of Heart Disease:
Depending on the type of heart disease
a person has, there are many treatment options available. However, some
standard approaches include adopting a healthier lifestyle, taking drugs, and
having surgery.
Medication: Typically given medications include
aspirin, beta-blockers, anticoagulants, and pain relievers. They halt development and avoid difficulties.
Surgery
When medication is ineffective at treating blockages
and other cardiac issues, surgery may be necessary. Common surgical procedures
include:
A) Coronary
artery bypass surgery (CABG): When
an artery is blocked, this procedure enables blood to flow to a certain area of
the heart. Coronary artery bypass grafting is the procedure that occurs the
most frequently. An unblocked blood artery can be repaired by a surgeon using a
healthy one from another body part. Procedures used for CABG can be Off-Pump
CABG or Open heart CABG, On-Pump CABG, Minimally invasive CABG and
Robot-assisted CABG.
B)
Coronary angiography: Coronary
angiography is a treatment that makes use of x-rays and a specific dye to see
how blood moves through the arteries in your heart. To find heart-related
coronary artery blockages, coronary angiography is conducted. This procedure
expands coronary arteries that are obstructed or narrowed. It is frequently
paired with the placement of a stent, a wire-mesh tube that facilitates better
blood flow, the procedure is called Balloon Angioplasty and Angioplasty
and Stent Placement.
C) Valve
replacement or repair: An ineffective valve can be replaced or
repaired by a surgeon. Procedures adopted for valve replacement or repair
surgeries can be Transcatheter aortic valve
replacement (TAVR), Transcatheter mitral valve repair
(TMVR), Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation and Balloon valvuloplasty.
D)
Repair Surgery:
Congenital cardiac defects, aneurysms, and other issues can all be fixed
surgically. Procedures can be Aneurysm repair, VAD or Ventricular assist
device Implantation, Heart valve repair or replacement, etc.
E) Device
Implantation: Pacemakers, balloon catheters, and other implants can support
blood flow and help control the heartbeat. Procedures are termed as Temporary
Pacemaker Implantation, Permanent Pacemaker Implantation, Single Chamber
Pacemaker Implantation, Dual Chamber Pacemaker Implantation, biventricular
pacemaker, ICD, or implantable cardioverter defibrillator Implantation.
F) Treatment
with lasers: Transmyocardial laser
revascularization or TMR is effective in treating angina. Other laser-based procedures can be Transmyocardial Laser Revascularization (TMLR),
Percutaneous Transmyocardial Revascularization (PTMR) and
Transmyocardial Revascularization and Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG)
Combined.
G)
Maze surgery: A surgeon can reroute electrical
signals through new channels. Atrial fibrillation may be treated using
this. This procedure can be done using Scalpel, Radiofrequency, and/or Cryoablation.
H)
Heart Transplant:
During a heart transplant, a sick
heart is swapped out for a healthier donor heart. Typically, patients who
require a heart transplant are those whose diseases have not sufficiently
improved with treatment.
When other methods of treating cardiac
issues have failed and heart failure has resulted, heart transplants are done.
Heart failure happens due to following reasons in adults
• heart
muscle deterioration (Cardiomyopathy)
• Severe Cardiovascular
disease
• Heart
valve dysfunction
• a birth
abnormality of the heart
• dangerously
recurring ventricular arrhythmias that are resistant to standard treatments
• a previous
heart transplant failed
Congenital heart defects or
cardiomyopathy are the two main causes of heart failure in children.
In certain medical centres, patients
with specific diseases may undergo a heart transplant along with another organ
transplant (multi-organ transplant).