Cancer, it’s diagnostics & Treatment Procedures
- 01 Nov, 2023
- 341
- Medical tourism
The uncontrolled spread of aberrant cells throughout the body is known as cancer. These cells have the ability to enter healthy body tissues. Numerous cancers can also be distinguished by the name of the tissue from which the aberrant cells first appeared (for instance, breast cancer, lung cancer, or colorectal cancer). Normal cell division takes place as an everyday occurrence, and cells typically die. Sometimes, injured or unrepaired cells proliferate and divide uncontrollably without dying, becoming cancer cells. This leads to the development of a mass of cancer cells. Cancer cells frequently break off from this initial clump of cells, move through the blood and lymphatic systems, and settle in other organs where they can restart the uncontrolled expansion cycle. It is one of the most dreaded illnesses in the world, which affects more than 11 lakh people annually in India alone. Whereas Globally, This chronic illness claims the lives of more than 10 million individuals every year.
The initial steps in detecting cancer are a physical examination and a
medical history, especially one that includes a history of symptoms. A
diagnostic and treatment plan should never be made in isolation in order to be
successful. To ensure that instances are found early when treatment is more
successful and there is a higher possibility of recovery, it must be connected
to an early detection program. Following are some of the diagnostic procedures
which help detect cancer.
Diagnostic Procedures:
Typical cancer tests include:
A physical examination: A doctor will examine your body and feel for any
changes or out-of-the-ordinary sensations. This is the simplest method of
detecting cancer.
Blood test: Cancer cells may emit chemicals that can be found in
a sample of blood. These blood tests are particularly useful for identifying
early-stage malignancies.
X-Ray: The extent of the malignant growths in the tissue is seen on an x-ray.
This is a crucial test for persons who exhibit symptoms that could indicate
their cancer has spread.
Test for Cancer Staging: This test shows the extent of the tumor's
dissemination. Treatment can be guided by staging.
Biopsy: A tissue sample is taken from a suspected cancerous region. Surgical
intervention or a needle and thread can be used to accomplish this.
CT Scan: Using X-rays, a CT scan produces images of the body. The chest, belly,
pelvis, and spine are the body parts that are most frequently pictured.
MRI Scans: It produces images of the brain and other bodily
organs using strong magnetic fields and radio waves. They frequently rule out
diseases like stroke, brain hemorrhage, and cancer.
PET Scan: PET Scan may help doctors pinpoint the tumor's
location throughout the body.
In
order to stage tumors, a variety of techniques are used, and each type of
cancer has its own unique staging standards. The NCI claims that the following
factors are typically taken into account in staging systems:
·
Size of the tumors and their number
·
the location of the main tumor
·
whether metastasis has occurred or not
·
Cancer spread to the lymph nodes, or lymph node involvement, etc.
Once
Diagnosed, following are the ways these malignancies can be restricted, treated,
or cured by Cancer Specialists/Surgeons or Oncology Specialists such as Medical
Oncologists, Surgical Oncologists and Radiation Oncologists.
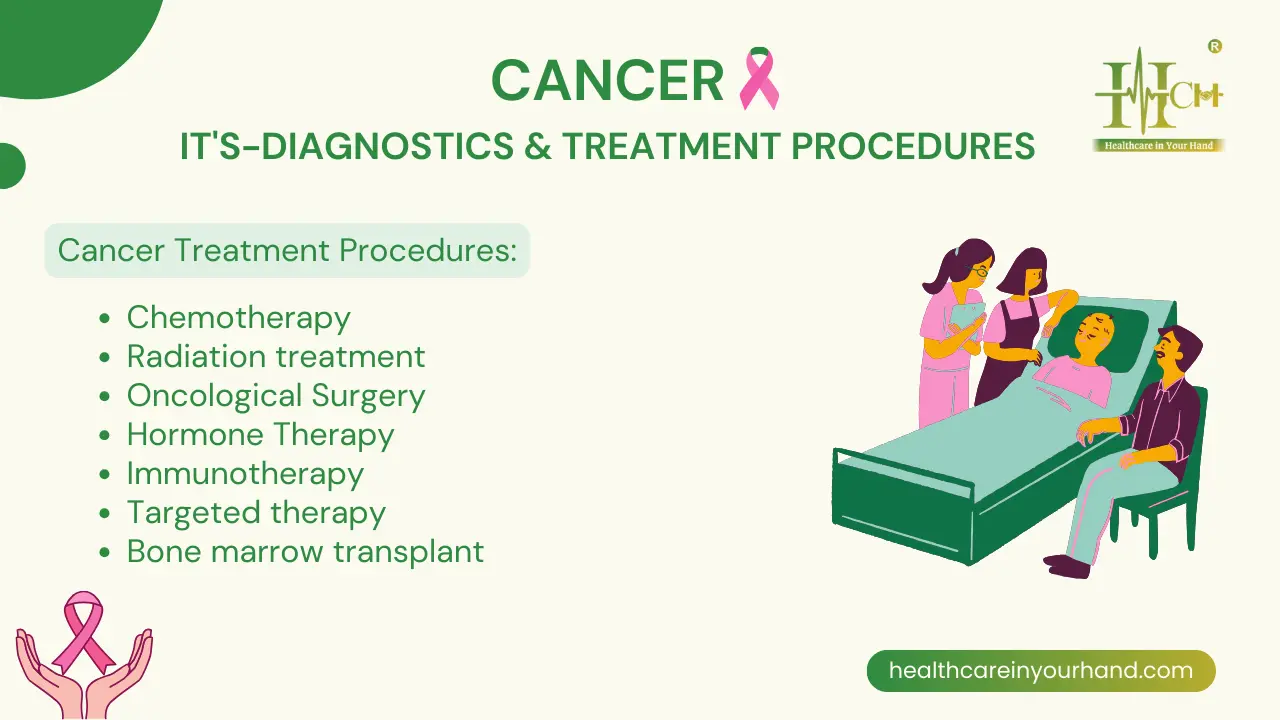
Cancer Treatment Procedures:
Radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and/or a combination of therapies are
all used as cancer treatments, along with surgery to remove the tumor. The
treatment's goal is to stop the cancer from recurring or metastasizing.
In an effort to stop their cancer from returning, some patients may also
receive immunotherapy or hormone therapy.
Depending on your situation, healthcare professionals may combine various
treatments. Typical cancer therapies include:
Chemotherapy: It is one of the most often used cancer treatments.
It kills cancer cells using potent medicines. Chemotherapy can be administered
orally or intravenously. In certain scenarios, doctors might be able to target
chemotherapy at the precise damaged location.
Radiation treatment: High levels of radiation are used in to eliminate
cancer cells. Chemotherapy and radiation therapy can also be combined.
Oncological Surgery: Non-spreading cancerous tumors may be removed through
surgery. Therapy may be suggested by your doctor. This procedure shrinks a
tumor before surgery or eliminates cancer cells that might still be present
after surgery. It is combined with chemotherapy or radiation.
Hormone Therapy: Sometimes, the use of hormones is
also recommended to treat cancer. For instance, those, who have
prostate cancer may be given hormones to keep testosterone levels, which
contribute to the disease, lower than normal.
Immunotherapy: It is a form of cancer treatment that activates your
body's defense mechanisms to combat the illness. Biological therapy is one name
for the treatment.
Targeted therapy: It focuses on the genetic alterations or mutations
that cause healthy cells to develop cancer.
Bone marrow transplant: BMT or stem cell replacement therapy, replaces
unhealthy stem cells with functional ones. Blood Oncologists uses your own
healthy stem cells during autologous transplantation. Whereas Stem cells from
another person are used in allogeneic transplants.
Oncology surgery or Onco surgery procedures applied on affected
Organs for cancer treatment are as follows:
Pancreatectomy: Your pancreas may be completely or partially removed.
Cancer and occasionally severe chronic pancreatitis are the main reasons why
it's done. Your digestive system may suffer permanent effects if all or part of
your pancreas is removed. You might have to start taking digestive enzymes and
insulin.
Pneumonectomy: One lung is surgically removed. It is the most
substantial lung removal surgery. This is most frequently used to remove
lung masses and tumors, such as non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Mastectomy: It is a surgical procedure, performed by breast oncology surgeons,
where entire breast tissue is removed from the breast. A mastectomy might be a possible course of
treatment for those with early-stage breast cancer. Another alternative
is lumpectomy, in which only the breast tumor is removed. For
preventing breast cancer recurrence, both procedures are equally beneficial.
These methods are studied and described under the separate subject of breast surgical oncology
Lobectomy: In a lobectomy, one lung lobe that has cancerous tumors is removed.
Lobes are components of each lung. While the left lung contains two lobes, the
right lung has three.
Thyroidectomy: The thyroid gland is surgically removed with this method, either entirely
or partially. Thyroid cancer, goiter, endocrine, or head and neck cancer can
all be treated using this surgery by ENT Oncologists.
Colectomy: The big bowel is removed during a colectomy. It entails the surgical
removal of the colon in any form, typically through segmental resection. Total
colectomy, which signifies the removal of the rectum as well as the large
intestine, is used in extreme situations.
Disarticulation: In this surgery, a limb is severed from the body entirely or in
part, usually through a joint.
Gamma Knife: Treatment for a lesion or tumor in the brain with
the Gamma Knife involves the use of extremely focused gamma ray beams. It
doesn't need to make an incision.
Cyber Knife: An alternative to radiation therapy for both
cancerous and non-cancerous tumors. It can be used as an alternative to surgery
or for patients with inoperable or surgically complicated tumors to treat
problems in all parts of the body, including the prostate, lung, brain, spine,
head & neck, liver, pancreas, and kidney. Treatments with the CyberKnife
usually take 1 to 5 sessions.
Proton Therapy/ proton beam therapy: It is a form of
radiation therapy that uses highly energetic protons (atoms with positive
charges) to harm the DNA of cancer cells. It is non-invasive, painless, and
precise to treat cancer in this way. It kills and stops the spread of cancer
cells by focusing on their genetic makeup.
Since, Cancer is termed as the most complex set of diseases, there are
many cancer institutes established across the world as Cancer Hospitals or
Oncology Hospitals which claims to provide best cancer
treatment in the world. In fact there are some organizations
that are dedicated to Cancer affecting particular body organ such as Lung Cancer
Hospitals, Liver Cancer Hospitals, etc.